Concrete Revolution: Crafting Sustainable Futures with Precast Infrastructure
Among the many building materials that are accessible, precast concrete is a reliable option for creating the framework of sturdy infrastructure. Precast concrete has several uses, from unmatched durability and quick construction to strict quality control and environmentally friendly methods. This article highlights the inherent advantages, practicality, and affordability of using precast concrete in infrastructure projects by examining its use in railroads, bridges, water management, and utility structures.
Advantages of Precast Concrete in Infrastructure Development
Examining the intrinsic benefits of precast concrete in creating infrastructure demonstrates how it has a revolutionary effect on construction techniques. Precast concrete is a strong option with qualities like sustainability, efficiency, and durability transforming modern infrastructure building.
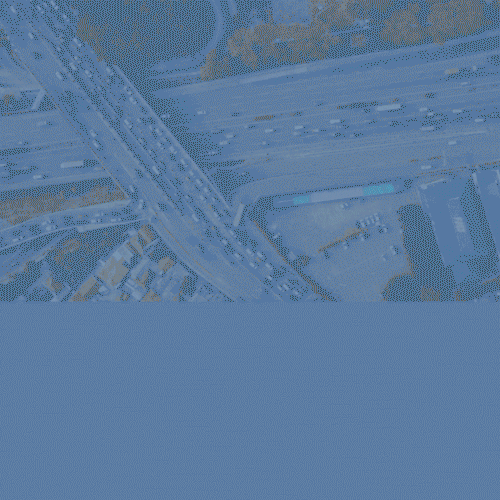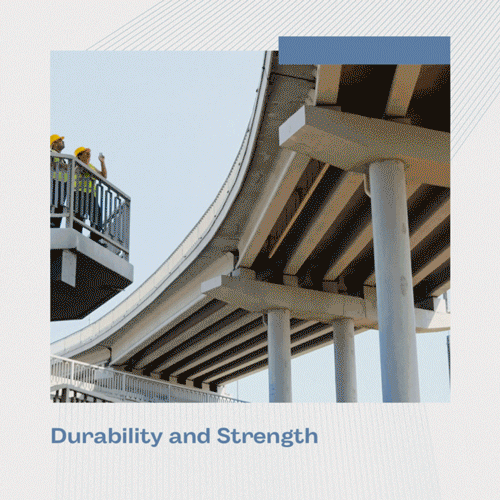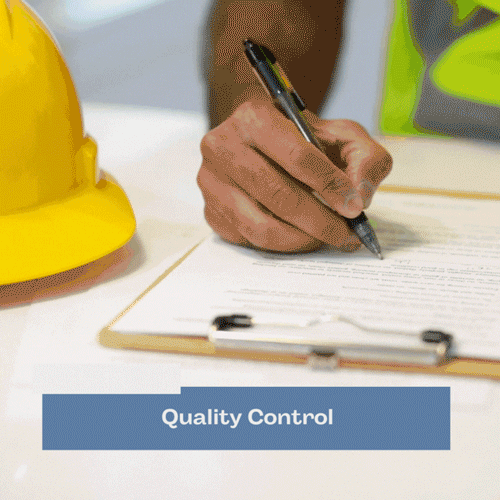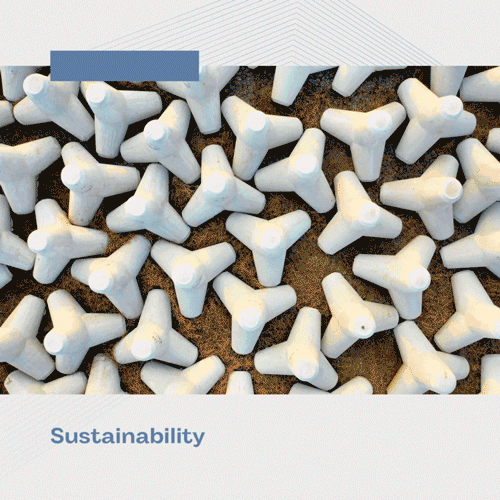
Durability and Strength
Precast concrete offers unmatched resistance to wear, corrosion, and severe weather compared to traditional building materials. Because of its innate strength, which guarantees structural integrity throughout time, it is the best material for infrastructure where durability and resilience are critical.
Efficiency and Speed
Building projects are completed much faster when precast concrete is used. When parts are produced in quality controlled environments off-site, less work needs to be done on-site, which speeds up project completion and lowers labor expenses.
Quality Control
Precast concrete is produced in a controlled atmosphere that ensures consistently high quality, even better than on-site casting. Strict quality controls are implemented during production to guarantee accuracy and compliance with industry norms.
Sustainability
The low waste generated during manufacturing and the possibilities for recycling make precast concrete an environmentally beneficial material. Its extended lifespan, robustness, and energy efficiency support environmentally friendly methods of building infrastructure.
Applications of Precast Concrete in Infrastructure
Bridges and Highways
Precast concrete is widely used in bridge construction because it provides flexible deck, girder, and abutment components. Its exceptional strength and resilience make it a dependable option that guarantees resilience and longevity across various bridge types.
Railways and Mass Transit Systems
Precast concrete is used in railways and mass transportation systems for stations, track systems, tunnels, and viaducts. In transportation situations with heavy traffic, its robustness guarantees longevity and safety.
Water and Wastewater Management
Precast concrete water management structures include sewage systems, treatment plants, and reservoirs. Being able to resist corrosion and keep their structural integrity, these structures offer long-lasting solutions for water distribution, storage, and treatment.
Utility Structures
Precast concrete provides stability, protection, and resilience against environmental variables, essential for utility structures such as communication towers and electrical substations.
Cost-Effectiveness and Long-Term Benefits
Gaining insight into the financial elements of precast concrete in infrastructure construction allows for a more nuanced understanding of its long-term benefits and cost-effectiveness. The comprehensive analysis of lifespan costs and long-term benefits highlights the sustainability and economic feasibility of using precast concrete in infrastructure projects, even though upfront costs may differ.
Initial Costs vs. Life Cycle Costs
Precast concrete in infrastructure is cost-effective when long-term expenditures are compared to upfront costs. Precast concrete may seem like a slightly more expensive initial investment than standard materials, but there are significant long-term benefits. Because precast concrete is resilient and long-lasting, it requires less maintenance, repair, and replacement, which lowers life cycle costs for infrastructure projects. Additionally, the shorter project durations produced by the expedited building timeframes made possible by precast concrete components mean lower labor costs and less disturbance to the surrounding region. Precast components can be quickly assembled, which reduces downtime and speeds up infrastructure projects, lowering costs in the long run.
Minimized Downtime
Additionally, precast concrete's inherent strength and durability result in a longer service life, which reduces the need for frequent repairs or replacements. This endurance improves cost-effectiveness since precast concrete infrastructure is more resilient to weather, wear, and structural deterioration. Precast concrete is a financially sensible option for infrastructure projects looking for long-term sustainability and economical resource utilization due to its minimal lifecycle costs and decreased requirement for continuing maintenance.
Investing in Tomorrow: The Smart Choice of Precast Concrete for Lasting Infrastructure
Precast concrete's incorporation into infrastructure development is a shining example of efficiency and creativity. Its many benefits—from unmatched durability and construction efficiency to strict quality control and cost-effectiveness—highlight its crucial role in modern building techniques. Precast concrete exhibits versatility and dependability in various applications, including water management, railroads, bridges, and utility structures. The benefits of precast concrete are undeniable as we embrace the future of infrastructure development; it provides an environmentally friendly, long-lasting, and financially sensible way to construct the framework for our changing society.